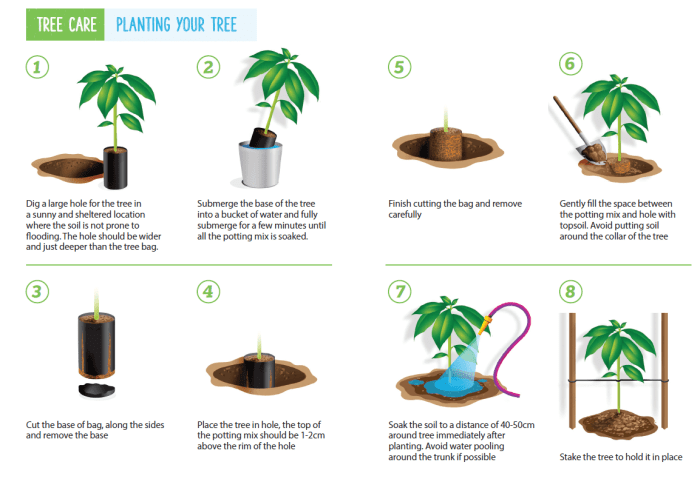
Long-Term Management and Pruning

How far apart to plant avocado trees – Regular pruning is crucial for the long-term health and productivity of avocado trees, especially when considering optimal spacing. Neglecting this aspect can lead to overcrowding, reduced yields, and increased susceptibility to disease. Proper pruning techniques ensure the tree maintains a desirable shape, allowing for sufficient sunlight penetration and air circulation, both vital for fruit development and disease prevention.Pruning techniques significantly impact light penetration and air circulation within the avocado tree canopy.
A well-pruned tree allows sunlight to reach all parts of the tree, promoting photosynthesis and fruit production. Adequate air circulation reduces humidity, which minimizes the risk of fungal diseases.
Pruning Techniques for Improved Light Penetration and Air Circulation
Proper pruning involves removing branches that are dead, diseased, or crossing each other. This opens up the canopy, allowing for better light penetration and air circulation. Thinning out the interior branches is also important, creating space for sunlight and air to reach the center of the tree. The techniques employed will vary depending on the age and size of the tree, but the overall goal remains consistent: to maintain a balanced, open canopy.
For example, a young tree might require selective pruning to establish a strong framework, while a mature tree might need more extensive thinning to prevent overcrowding. This could involve removing up to 30% of the branches annually, focusing on the interior branches first.
Yo, so spacing your avocado trees depends on the variety, but generally, think good airflow. Need some citrusy vibes in your life while you’re figuring that out? Check out this awesome guide on how to plant lemon tree in pot – super helpful! Then, get back to those avocados and remember, proper spacing means happy, healthy trees, brah.
Managing Tree Size and Shape to Prevent Overcrowding
Maintaining the appropriate size and shape of the avocado tree is essential to prevent overcrowding and ensure optimal yield. Regular pruning, coupled with careful selection of tree varieties suited to the available space, is crucial in this process. For instance, choosing a dwarf or semi-dwarf variety for a smaller garden is a proactive approach to size management. Techniques like heading back (cutting back the terminal buds) can control the height of the tree, while thinning out lateral branches can help maintain a desired width.
These actions prevent excessive growth and maintain an open canopy, preventing the shading and crowding that can lead to reduced yields and increased susceptibility to disease. Regular monitoring and selective pruning are key to this long-term management strategy. A well-managed tree will maintain a vase-like shape, allowing for even light distribution and optimal fruit production.
Effect of Spacing on Pest and Disease Management
Proper spacing between avocado trees significantly impacts pest and disease management within an orchard. The density of planting directly influences the microclimate, airflow, and overall health of the trees, creating conditions that either promote or hinder the spread of pests and diseases.Appropriate spacing improves disease control and reduces pest infestations by promoting better air circulation and sunlight penetration. This reduces humidity levels, creating a less favorable environment for many fungal pathogens and pest species that thrive in damp, shaded conditions.
Reduced humidity minimizes leaf wetness duration, a critical factor in the development of many fungal diseases. Increased sunlight also helps to dry foliage more quickly.
Airflow and Disease Spread
Adequate spacing between trees allows for better air circulation, which helps to dissipate spores and other disease-causing agents. In densely planted orchards, the lack of airflow can create a humid microclimate that favors the rapid spread of diseases like Phytophthora root rot, which is a devastating disease affecting avocado trees. Imagine a dense orchard where spores released from an infected tree are easily carried to neighboring trees by the slightest breeze.
In contrast, widely spaced trees allow for greater dispersal of these spores, reducing the likelihood of widespread infection. Studies have shown a significant correlation between tree density and the incidence of Phytophthora root rot, with denser plantings exhibiting higher infection rates.
Pest Infestation in Dense vs. Wide Plantings
Pest management strategies differ significantly between densely and widely spaced orchards. Dense plantings often necessitate the use of more frequent and potentially more aggressive chemical treatments to control pest populations. The close proximity of trees makes it easier for pests to spread, requiring more intensive interventions to prevent widespread damage. For example, in a densely planted avocado orchard, the avocado thrips might proliferate rapidly, leading to a need for repeated insecticide applications.
In contrast, widely spaced orchards allow for better monitoring and targeted treatment of pest infestations. Natural enemies of pests may also be more effective in widely spaced orchards due to improved habitat and reduced pesticide use. This allows for integrated pest management strategies that rely more on biological control methods, reducing reliance on harmful chemicals. For instance, introducing beneficial insects like predatory mites could be more successful in a less dense orchard, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Disease Management Strategies, How far apart to plant avocado trees
Disease management in densely planted orchards often requires more proactive and intensive approaches. This might include prophylactic fungicide applications, even before disease symptoms appear, to prevent outbreaks. Regular monitoring and early detection are crucial, as the rapid spread of diseases in dense plantings necessitates swift intervention. In contrast, widely spaced orchards often allow for more targeted disease management strategies.
The improved microclimate reduces the need for frequent fungicide applications. Furthermore, the easier access to individual trees allows for more precise diagnosis and treatment of infected plants, potentially preventing the spread of disease to the rest of the orchard. This targeted approach minimizes environmental impact and reduces the development of fungicide resistance.
Q&A: How Far Apart To Plant Avocado Trees
What type of soil is best for avocado trees?
Well-draining soil rich in organic matter is ideal. Avocados hate soggy feet!
How often should I water my avocado trees?
Regular watering, especially during dry spells, is crucial, but avoid overwatering.
Can I grow avocado trees in containers?
Yes, but choose a dwarf variety and a large enough pot. Regular repotting might be necessary.
What are common pests and diseases that affect avocado trees?
Common issues include root rot, avocado leaf blotch miner, and various fungal diseases. Proper spacing helps mitigate some of these.