Planting the Cocoa Tree Seedlings: How To Plant A Cocoa Tree

How to plant a cocoa tree – Alright, so you’ve got your healthy cocoa seedlings, ready to hit the ground running. Planting them right is key, it’s like giving them a VIP pass to a life of delicious chocolate-making! Get it wrong, and you’re looking at a much slower growth, or worse, a dead plant. So pay attention, Medan style!
Planting cocoa seedlings isn’t rocket science, but there’s a proper way to do it to ensure your trees thrive. Think of it like making a perfect Nasi Goreng – you need the right ingredients and the right technique for the best results.
Cocoa Seedling Planting Techniques
Here’s the lowdown on getting your cocoa seedlings into the ground like a pro. We’ll cover depth, spacing, and those all-important support structures. Remember, this is about setting your cocoa up for success from day one!
- Depth: Plant your seedlings at the same depth they were growing in their nursery pots. Don’t bury them too deep, or the stem might rot. Think of it like this: the soil line on the seedling should be the same as the soil line in the ground. Too deep, and you’ll suffocate the roots; too shallow, and the seedling might topple over.
- Spacing: Spacing depends on the variety of cocoa and your local conditions, but a general guideline is 2.5 to 3 meters apart. This gives each tree enough room to grow its roots and branches without competing for resources. Imagine it like giving each tree its own private little plot of land in your cocoa plantation.
- Support Structures: Young cocoa seedlings are delicate. Use stakes to support them, preventing them from being damaged by wind or heavy rain. Tie the seedling gently to the stake using soft material, avoiding any tight bindings that could damage the stem. Think of it as giving your little cocoa tree a friendly hug, helping it stand tall and strong.
Ideal Soil Level Around the Stem, How to plant a cocoa tree
Picture this: your cocoa seedling stands tall and proud, nestled in the earth. The soil level around the base of the stem is even with the soil line from the nursery pot. There’s no soil piled up against the stem, and the roots are gently covered. The area around the base is nicely mulched to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
It’s a happy, healthy little cocoa tree, ready to grow!
Successfully planting a cocoa tree requires careful attention to shade and soil conditions. However, for those lacking the space or climate for a real cocoa tree, a visually appealing alternative might be a fake banana tree plant , offering a similar tropical aesthetic. Returning to the real thing, proper irrigation is crucial for cocoa tree growth, ensuring consistent moisture without waterlogging.
Common Planting Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced farmers can make mistakes. Knowing what to avoid can save you time, effort, and cocoa trees. Let’s avoid some common pitfalls.
- Planting too deep: This can lead to root rot and the death of the seedling. Always plant at the same depth as the nursery pot.
- Planting too shallow: The seedling becomes unstable and vulnerable to wind and weather. Ensure the roots are well-covered and the seedling is securely planted.
- Poor spacing: Overcrowding leads to competition for resources, resulting in smaller, weaker trees. Proper spacing is crucial for optimal growth.
- Neglecting support structures: Young seedlings are fragile and need support to grow straight and strong. Use stakes and soft ties to protect them from damage.
- Improper mulching: Mulching helps retain moisture and suppress weeds, but piling it too high against the stem can lead to rot. Keep the mulch a few centimeters away from the stem.
Harvesting and Processing Cocoa Beans

Medan style, right? So, picture this: you’ve waited patiently, your cocoa trees are thriving, and it’s finally harvest time! Getting those beans from the tree to your cup of delicious chocolate is a journey, and it all starts with knowing when and how to harvest those precious pods.
Mature Cocoa Pods: Appearance and Size
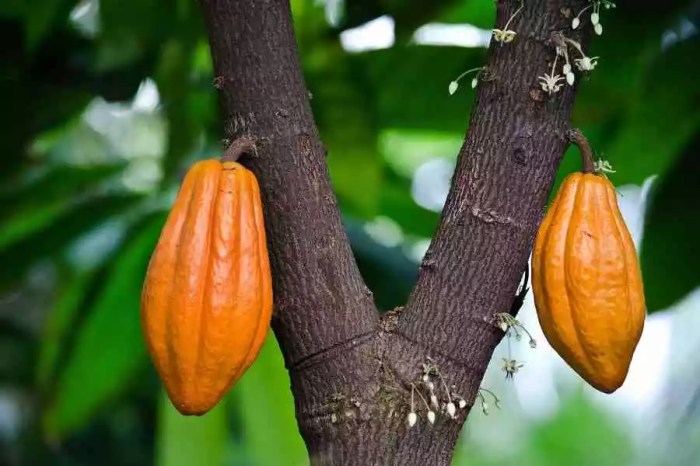
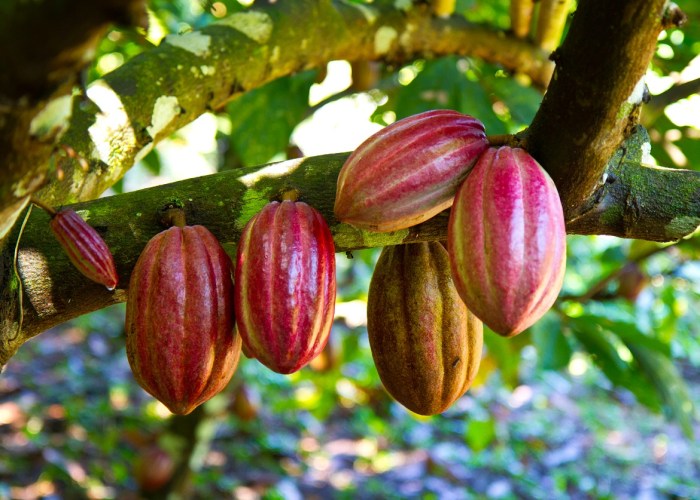
Imagine plump, football-shaped pods hanging from the cocoa tree. These aren’t your average fruits; mature pods are typically 6 to 12 inches long, depending on the variety and growing conditions. Their color varies wildly, from a vibrant yellow-orange to a deep reddish-brown, almost purple in some cases. The skin is usually thick and leathery, often with a slightly rough texture.
You’ll notice a distinctive ribbed pattern on the surface, and sometimes even slight cracks, indicating they’re ready for picking. A ripe pod will feel heavy for its size, and sometimes you can even hear the beans rattling inside if you shake it gently.
Harvesting, Fermenting, and Drying Cocoa Beans
The process of transforming those vibrant pods into the cocoa beans we know and love involves several crucial steps. Here’s the Medan-style lowdown:
- Harvesting: Use a sharp machete or a similar tool to carefully cut the pods from the tree, avoiding damage to the branches. This needs to be done with a steady hand and a bit of experience to get it right.
- Opening the Pods: Once harvested, use a machete or special cocoa pod opener to carefully split the pods open. Inside, you’ll find rows of glistening white cocoa beans embedded in a sweet, pulpy substance.
- Fermentation: This is where the magic happens! The beans are piled in heaps, often covered with banana leaves, to begin the fermentation process. This typically lasts for 5-7 days, during which the pulp ferments, creating the characteristic chocolate flavor. The temperature rises significantly during this process, so monitoring is crucial. Different fermentation methods exist; some use boxes, others just heaps on the ground.
The duration and specific technique impact the final flavor profile.
- Drying: After fermentation, the beans are spread out on trays or mats to dry. This can take several days, depending on the weather conditions. Regular turning is essential to ensure even drying. The beans are considered dry when they snap easily when broken, reaching a moisture content of around 7%. Sun drying is common, but some farmers use mechanical dryers for more consistent results.
Cocoa Bean Processing Methods and Their Impact on Quality
Different methods of processing impact the final product. Traditional methods, often sun-drying and basic fermentation, produce beans with a more rustic, earthy flavor. More advanced techniques, such as controlled fermentation in boxes and mechanical drying, can lead to more consistent quality and a wider range of flavor profiles. For example, faster fermentation can result in a more acidic and fruity cocoa, while slower fermentation might give a more bitter, robust flavor.
The choice of processing method often depends on factors like available resources, climate, and the desired final product. Larger farms might utilize mechanical dryers and controlled fermentation for consistency, while smaller farms might rely on traditional methods.
FAQ Section
What is the best time of year to plant cocoa trees?
The ideal planting time depends on your region’s climate, but generally, it’s best to plant during the rainy season to ensure adequate moisture for establishment.
How long does it take for a cocoa tree to produce fruit?
It typically takes 3-5 years for a cocoa tree to begin producing a significant cocoa bean harvest.
How often should I fertilize my cocoa trees?
Regular fertilization is crucial. A balanced fertilizer should be applied every 2-3 months, adjusting the amount based on soil test results and tree size.
What are some common pests and diseases that affect cocoa trees?
Common pests include cocoa pod borers and mealybugs. Diseases include black pod rot and witches’ broom. Regular inspection and preventative measures are essential.