Polka Dot Plant Seed Characteristics
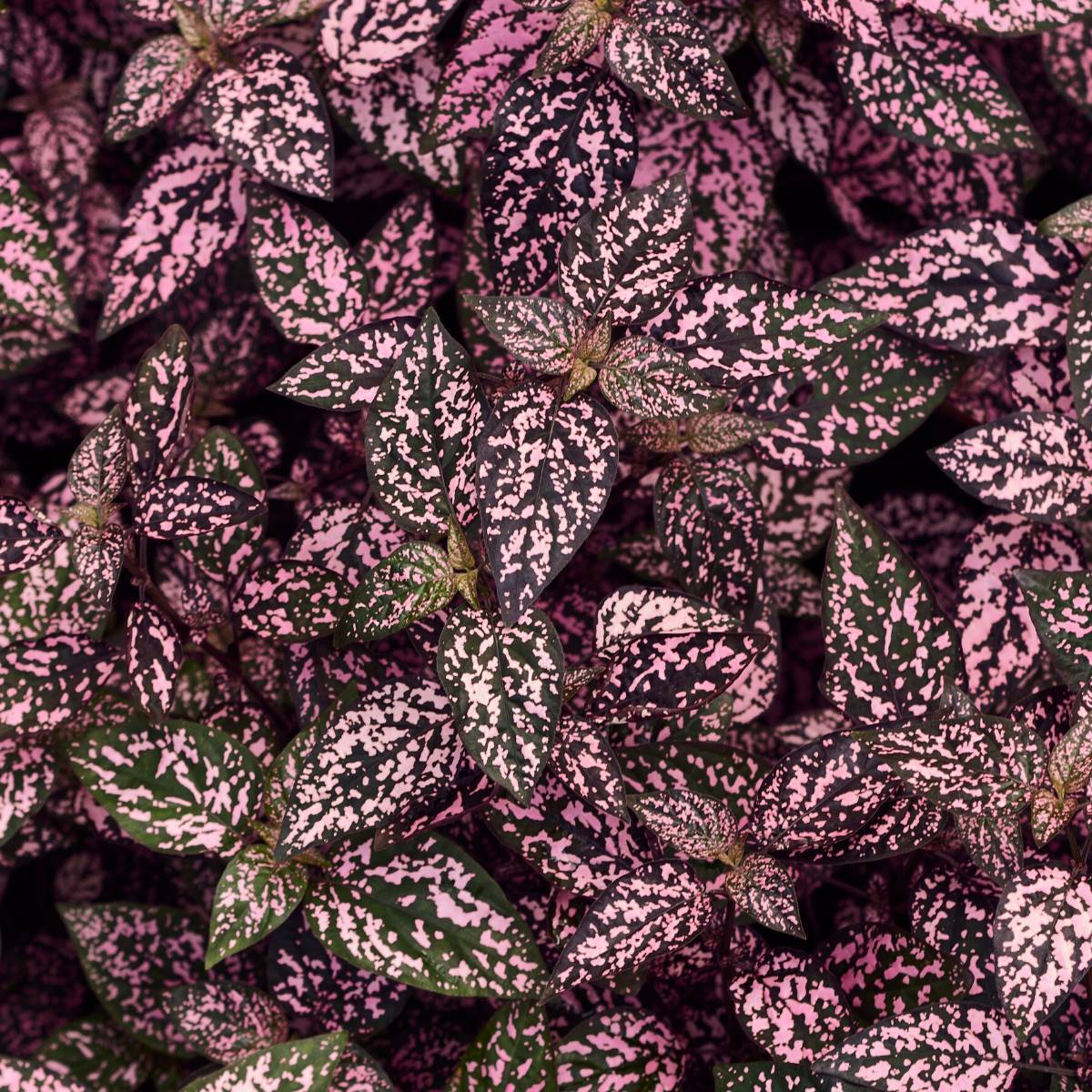

Polka dot plant seeds, scientifically known asHypoestes phyllostachya*, are relatively small and possess distinct characteristics that differentiate them from seeds of similar-looking plants. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for successful propagation and cultivation. Their size, shape, and germination requirements influence planting techniques and overall yield.
Polka dot plant seeds are typically minute, ranging from 0.5 to 1 millimeter in length. Their shape is generally ovate or oblong, slightly flattened, and possesses a fine, almost smooth texture. The color is usually a dark brown or black, sometimes exhibiting a slightly glossy appearance. These seeds lack the prominent wings or hairs found on many other plant seeds, facilitating their dispersal through different methods.
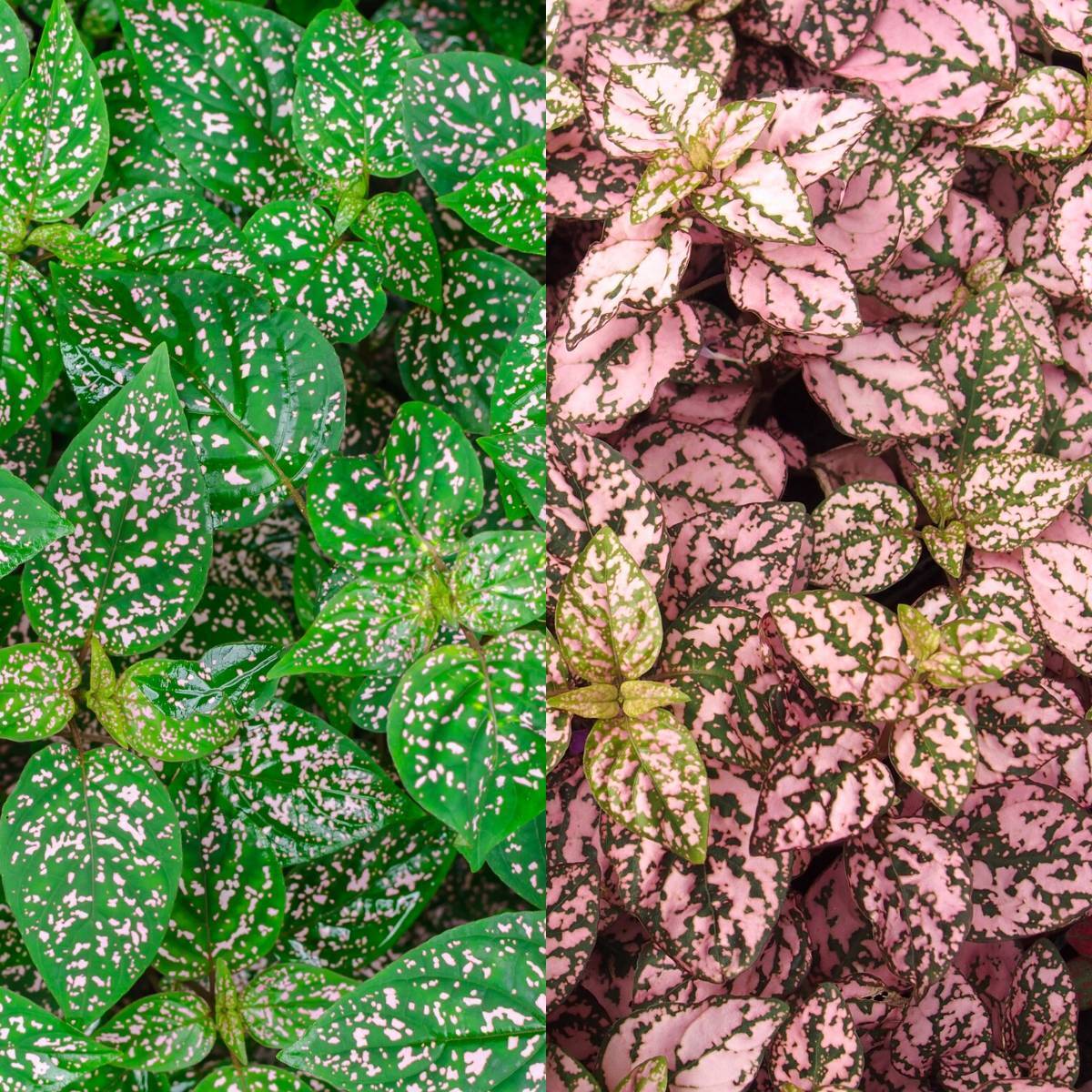
Seed Size, Shape, and Color Comparison, Polka dot plant seeds
Compared to seeds of similar-looking plants such as Coleus (
-Plectranthus scutellarioides*), polka dot plant seeds are significantly smaller. Coleus seeds, while also dark-colored, are often larger and more irregularly shaped. Furthermore, the texture might be slightly rougher due to surface irregularities. Other similar plants, like certain types of Alternanthera, produce even smaller seeds, but these tend to be lighter in color, often appearing more reddish-brown than the deep brown of
-Hypoestes phyllostachya* seeds.
The differences in size, shape, and color are key identifiers when distinguishing between these various seeds.
Germination Rates Under Varying Conditions
Germination success for polka dot plant seeds is heavily influenced by environmental factors. Optimal conditions promote rapid and consistent germination, while suboptimal conditions can lead to significantly reduced germination rates or complete failure. The following table summarizes germination rates observed under different light, temperature, and moisture levels. These values are based on controlled experiments and represent average results. Actual outcomes may vary slightly based on seed quality and other environmental nuances.
Polka dot plant seeds are tiny, requiring careful handling for successful germination. Spacing is crucial for healthy growth, much like considering how far apart to plant aspen trees, as detailed in this helpful guide: how far apart to plant aspen trees. Proper spacing for polka dot plants prevents overcrowding and ensures each seedling receives adequate sunlight and nutrients for vibrant foliage.
| Condition | Light (Hours/Day) | Temperature (°C) | Moisture Level | Germination Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal | 12-16 | 20-25 | Moist (but not waterlogged) | 85-95 |
| Low Light | 6-8 | 20-25 | Moist (but not waterlogged) | 50-65 |
| Low Temperature | 12-16 | 15-18 | Moist (but not waterlogged) | 60-75 |
| Dry Conditions | 12-16 | 20-25 | Dry | <5 |
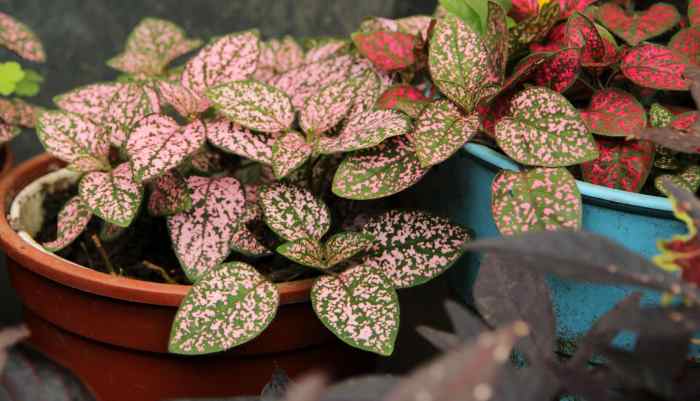
Sowing Polka Dot Plant Seeds

Successfully germinating polka dot plant seeds indoors requires attention to detail in several key areas: proper seed preparation, suitable soil composition, and precise planting techniques. Following these steps maximizes germination rates and establishes healthy seedlings ready for transplanting.Polka dot plant seeds are notoriously small, demanding a delicate approach to sowing. Successful germination hinges on providing the optimal environment to stimulate root and shoot development.
Ideal Soil Mix for Polka Dot Plant Seed Germination
A well-draining, yet moisture-retentive, soil mix is crucial for polka dot plant seed germination. Poor drainage leads to root rot, while insufficient moisture hinders germination. An ideal blend combines equal parts of seed-starting mix, perlite, and vermiculite. The seed-starting mix provides essential nutrients, while perlite and vermiculite improve aeration and drainage, preventing waterlogging. This combination ensures the delicate seeds receive adequate moisture without suffocating in overly saturated soil.
Seed Depth and Spacing
Planting depth and spacing directly impact germination success and seedling development. Polka dot plant seeds should be sown very shallowly, barely covering them with the soil mix. Burying them too deeply deprives them of sufficient light, hindering germination. Ideal spacing between seeds should be approximately 1 inch apart to allow for adequate root development and prevent overcrowding.
Overcrowding leads to competition for resources, resulting in stunted growth and weaker plants.
Optimal Setup for a Polka Dot Plant Seed Tray
Visualize a standard seed tray with small, individual cells. Each cell should be filled with the prepared soil mix, described above, leaving about ¼ inch of space from the top. Polka dot plant seeds are then sprinkled evenly across the surface of the soil in each cell, followed by a very light dusting of the same soil mix, barely covering the seeds.
The tray should then be gently watered from below using a tray of water, allowing the soil to absorb moisture from the bottom up. This prevents the seeds from being dislodged or washed away. Finally, the tray is covered with a clear plastic dome or humidity cover to maintain high humidity, essential for successful germination. This creates a miniature greenhouse effect, mimicking the warm, humid conditions found in their native environment.
The cover should be vented daily to prevent fungal growth.
Polka Dot Plant Seed Germination

Successful polka dot plant seed germination hinges on replicating the plant’s natural environment. Understanding the process, potential pitfalls, and preventative measures is crucial for achieving high germination rates and healthy seedlings. This section details the key aspects of polka dot plant seed germination, offering practical guidance for both novice and experienced gardeners.Polka Dot Plant Seed Germination is a process that begins with imbibition, where the seed absorbs water and swells.
This triggers metabolic activity within the seed, initiating the growth of the embryo. The radicle, or embryonic root, emerges first, anchoring the seedling and absorbing nutrients. Subsequently, the plumule, or embryonic shoot, develops, pushing upwards towards the light. Optimal germination typically occurs within 1-3 weeks under ideal conditions, but this timeframe can vary based on factors like seed viability, temperature, and moisture levels.
Factors Affecting Germination
Several factors significantly influence the success of polka dot plant seed germination. Maintaining consistent warmth, sufficient moisture, and adequate light are key to promoting healthy seedling development. Conversely, factors like improper watering, insufficient light, or excessively low or high temperatures can hinder germination. Seed quality, including seed age and storage conditions, also plays a critical role. Seeds stored improperly or for extended periods may exhibit reduced viability, resulting in lower germination rates.
Troubleshooting Germination Issues
Successful germination relies on addressing potential problems proactively. Early identification and resolution of issues are key to maximizing germination success.
- Poor Germination Rate: This could indicate low seed viability, improper sowing depth, or unsuitable environmental conditions (temperature, moisture, light). Consider using fresh seeds, adjusting sowing depth, and optimizing environmental factors.
- Seed Rot: Overwatering or poorly draining soil can lead to seed rot. Ensure well-draining soil and avoid overwatering, allowing the soil surface to dry slightly between waterings.
- Slow Germination: Low temperatures or insufficient light can slow down the germination process. Maintain a consistently warm temperature (ideally between 70-75°F or 21-24°C) and provide adequate, indirect light.
- No Germination: This could be due to several factors including dormant seeds, old seeds, or improper handling. Using fresh seeds, checking seed viability before sowing, and ensuring proper sowing techniques can help prevent this.
Preventative Measures for Successful Germination
Employing preventative measures is crucial for maximizing germination rates and obtaining robust seedlings. These measures focus on optimizing environmental conditions and selecting high-quality seeds.
- Seed Selection: Choose fresh, high-quality seeds from reputable suppliers. Check the seed packet for germination rates and sow by date for best results.
- Soil Preparation: Use a well-draining seed-starting mix that retains moisture but avoids waterlogging. Sterilizing the soil beforehand can prevent fungal diseases.
- Temperature Control: Maintain a consistent temperature range of 70-75°F (21-24°C). A heat mat can help maintain optimal temperatures, particularly in cooler environments.
- Moisture Management: Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Regularly check the moisture level and water as needed. A humidity dome can help maintain high humidity levels, particularly during the initial stages of germination.
- Light Exposure: Provide adequate indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch delicate seedlings. Supplemental grow lights can be beneficial, especially during winter months or in low-light conditions.
Growing Polka Dot Plants from Seed
Cultivating polka dot plants from seed offers a rewarding experience, but success hinges on understanding and addressing potential challenges. While relatively straightforward, certain hurdles can impede germination and seedling development, ultimately impacting the overall yield and plant health. Careful attention to environmental conditions and proactive disease management are key to achieving robust growth.
Challenges in Polka Dot Plant Seed Germination and Growth
Several factors can hinder the successful cultivation of polka dot plants from seed. These include issues related to germination, seedling establishment, and disease susceptibility. Slow or uneven germination is a common problem, often linked to improper sowing techniques or unsuitable environmental conditions. Furthermore, damping-off, a fungal disease, can decimate young seedlings before they have a chance to establish strong root systems.
Finally, inadequate light, nutrient deficiencies, and pest infestations can also compromise plant growth and overall vigor.
Solutions for Overcoming Common Problems
Addressing the challenges associated with growing polka dot plants from seed requires a multifaceted approach. Employing proper sowing techniques, ensuring optimal environmental conditions, and implementing preventative disease management strategies are crucial. For instance, using a well-draining seed-starting mix prevents waterlogging, a primary cause of damping-off. Maintaining consistent soil moisture, providing adequate light, and utilizing appropriate ventilation further minimize the risk of fungal diseases.
Furthermore, regular monitoring for pests and prompt intervention with organic control methods can safeguard seedling health.
Organic Disease Prevention in Polka Dot Plant Seedlings
Organic methods offer effective and environmentally friendly solutions for preventing diseases in polka dot plant seedlings. These approaches prioritize building healthy plants through soil health improvement and biological control. For example, using compost-amended potting mix enhances soil structure and provides beneficial microbes that compete with pathogens. Copper fungicides, though considered less toxic than synthetic counterparts, should be used judiciously and according to label instructions.
Practicing good sanitation, such as sterilizing seed-starting trays and tools, is crucial in preventing the spread of fungal diseases. Regularly inspecting seedlings for signs of disease and promptly removing affected plants can also help contain outbreaks.
Common Problems, Causes, and Solutions for Polka Dot Plant Seedlings
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damping-off | Fungal pathogens, overwatering, poor drainage | Improve drainage, reduce watering, use fungicide (e.g., copper fungicide) | Sterilize seed-starting mix and containers, ensure good air circulation |
| Slow Germination | Improper sowing depth, low temperatures, insufficient light | Sow seeds at the correct depth, maintain optimal temperature (70-75°F), provide adequate light | Use a heat mat, provide supplemental light, ensure proper seed depth |
| Leggy Seedlings | Insufficient light, overcrowding | Provide supplemental light, thin seedlings to reduce overcrowding | Ensure adequate spacing during sowing, use grow lights |
| Nutrient Deficiencies | Poor soil quality, lack of fertilization | Use a balanced fertilizer formulated for seedlings, amend soil with compost | Use a high-quality seed-starting mix, fertilize regularly |
General Inquiries: Polka Dot Plant Seeds
How long do polka dot plant seeds take to germinate?
Germination typically takes 1-3 weeks, depending on conditions.
Can I start polka dot plant seeds outdoors?
It’s best to start them indoors for better control over conditions, then transplant outdoors after the last frost.
How often should I water polka dot plant seedlings?
Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Water when the top inch of soil feels dry.
What type of light do polka dot plants need?
Bright, indirect light is ideal. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.